
Diabetic Foot Complications
Diabetic foot infections
Diabetic foot ulcers
Charcot arthropathy
Epidemiology
5 year mortality
- diabetic foot ulcer 30%
- diabetic amputation 70%
20% of patients with diabetic foot ulcer will undergo an amputation
Pathophysiology
1. Neuropathy
2. Peripheral vascular disease
3. Immunopathy
Neuropathy
Most important factor in foot disease caused by
- glycosylation of nerves
- ischaemia
| Sensory | Autonomic | Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Stocking distribution |
20 – 40% of Diabetics |
Loss of intrinsic muscle balance |
|
Semmes Weinstein 5.07 monofilament - applies 10gm of force - tip pressed against skin until starts to bend - patient asked if they can feel it - 90% of patients who are able to feel won’t ulcerate |
Skin dry / scaly / cracked Easier access for bacteria |
Claw and hammer toes Increased risk of plantar ulcers |
Peripheral vascular disease
50% of diabetic foot ulcers have peripheral vascular disease
| Large Vessel Disease | Small vessel disease |
|---|---|
|
Different to non diabetic population - younger age - at or below knee - diffuse and longer occlusions |
Microangiopathy
|
|
Vascular claudication Hindfoot ulcers |
Delayed ulcer healing |
Immunopathy
Good blood sugar control and nutrition improves healing
- HbA1C
- total protein > 6 g/dl or 60 g/L
- albumin > 3.5 g/dL or 35 g/L
- lymphocyte count > 1500 /mm3
- transferrin < 200mg/dl
Management
Multidisciplinary approach
Endocrinologist +/- diabetic nurse - glycemic control crucial
Podiatrist - non-surgical debridement / orthoses
Plaster technicians - total contact cast
Vascular surgeon
Orthopedic surgeon - total contact cast / surgical debridement / foot reconstruction / amputation
Infectious disease consultant - infections / non healing ulcers
Diabetic Foot Care
Daily foot hygiene
No walking barefoot
Immediate attention to blisters / ulcers
Custom shoes / orthoses
Infections
| Microbiology | Antibiotics |
|---|---|
|
Acute mild infections - usually mono microbial - commonly S Aureus, Strep |
Combination oral antibiotics - Augmentin Duo Forte - Cephalexin plus Metronidazole - Ciprofloxacin plus Clindamycin (Penicillin Allergy) |
|
Chronic infections / ulcers - polymicrobial - gram positive cocci (Staph; Group B Strep) - gram negative (E Coli; Pseudomonas) - Anaerobes (ischaemic limbs, Bacteriodes fragilis) |
Severe infections - intravenous antibiotics - Timentin / Pip-Taz - Ciprofloxacin - Clindamycin |
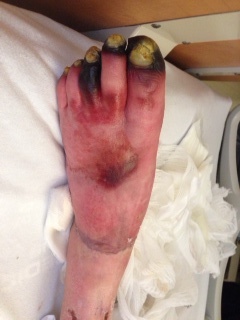
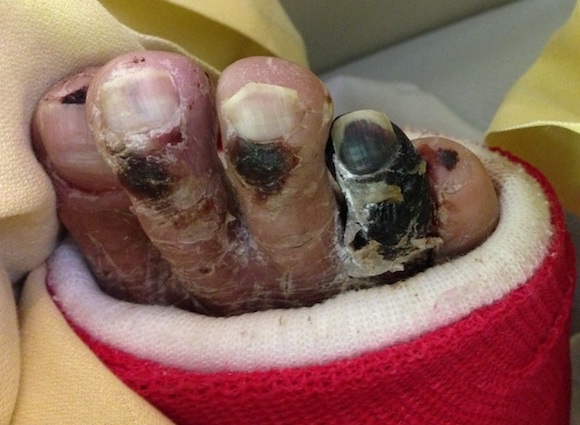
Diabetic foot ulcers
Wagner Classification
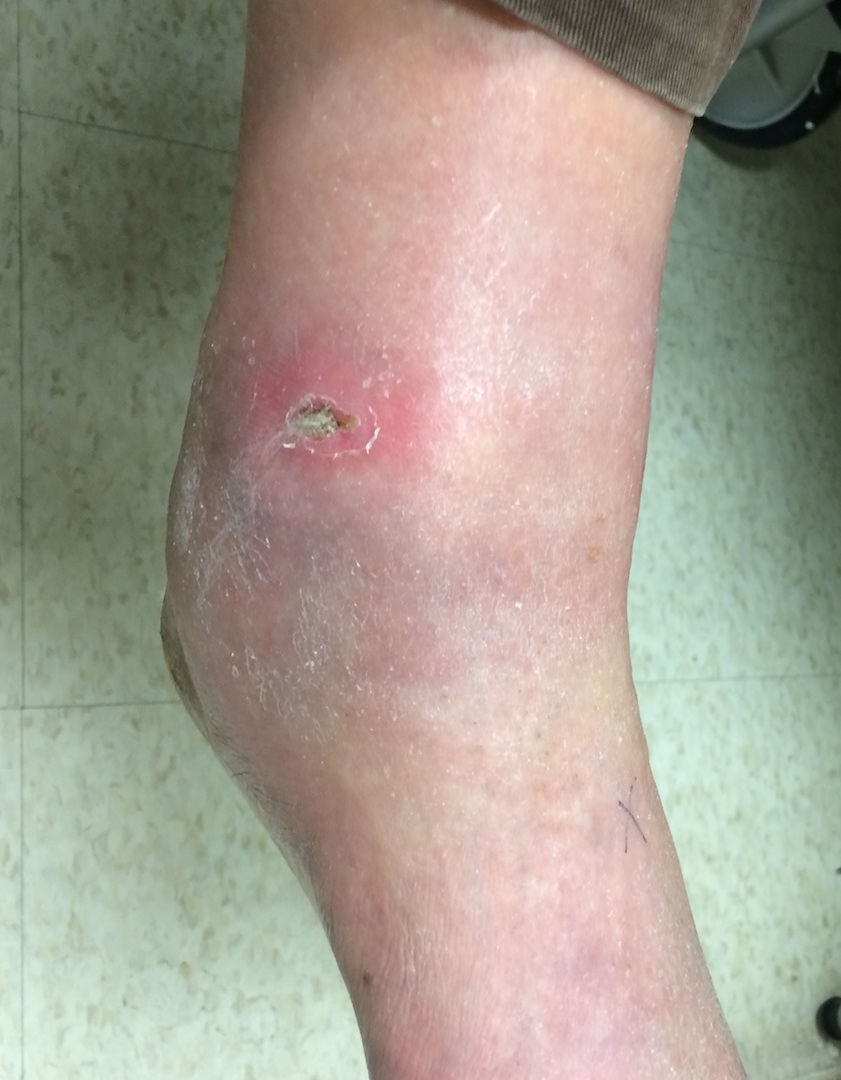
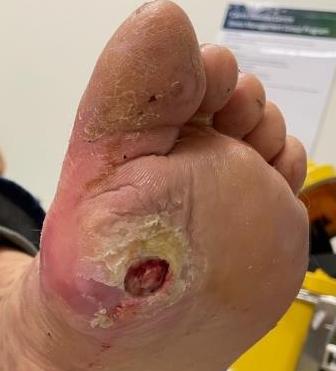
| Grade 0 | Grade I | Grade II |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure area | Superficial ulceration |
Deep ulceration Probes to tendon / capsule |
| Footwear modification |
Local treatment Footwear modification |
Total contact cast |
 |
 |
 |
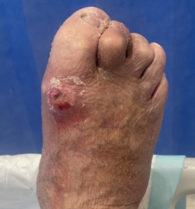
| Grade III | Grade IV | Grade V |
|---|---|---|
|
Deep ulceration + Secondary infection |
Partial foot gangrene | Whole foot gangrene |
|
Amputation Hyperbaric oxygen |
Amputation | |
 |
 |
 |
University of Texas Classification
| Grade | Stage |
|---|---|
|
1 Preulcerative 2 Superficial Wound 3 Deep wound penetrating to capsule or tendon 4 Deep penetrating to bone or joint |
A Clean B Non ischemic Infected C Ischemic Noninfected D Ischemic Infected |
Perfusion
| Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) | Transcutaneous O2 Measurement (TcPO2) | Toe Blood Pressure | Angiogram |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ABI: Ankle / Brachial Systolic BP at ankle and arm Normal 0.9 - 1.3 |
Electrode placed on warmed foot Affected by edema/ infection / neuropathy |
Plethysmography | |
|
<0.9 suggests PVD May be falsely elevated by calcified vessels |
<25 mmHg = unlikely to heal | >30 mmHg = good wound healing potential |
- systematic review
- transcutaneous oxygen measurement predicts wound healing and amputation
- ABI predictive of amputation but not wound healing
Infection / osteomyelitis
Xray / MRI / probe to bone / ESR > 70

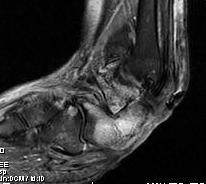
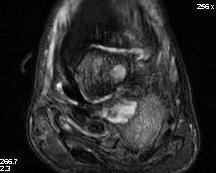
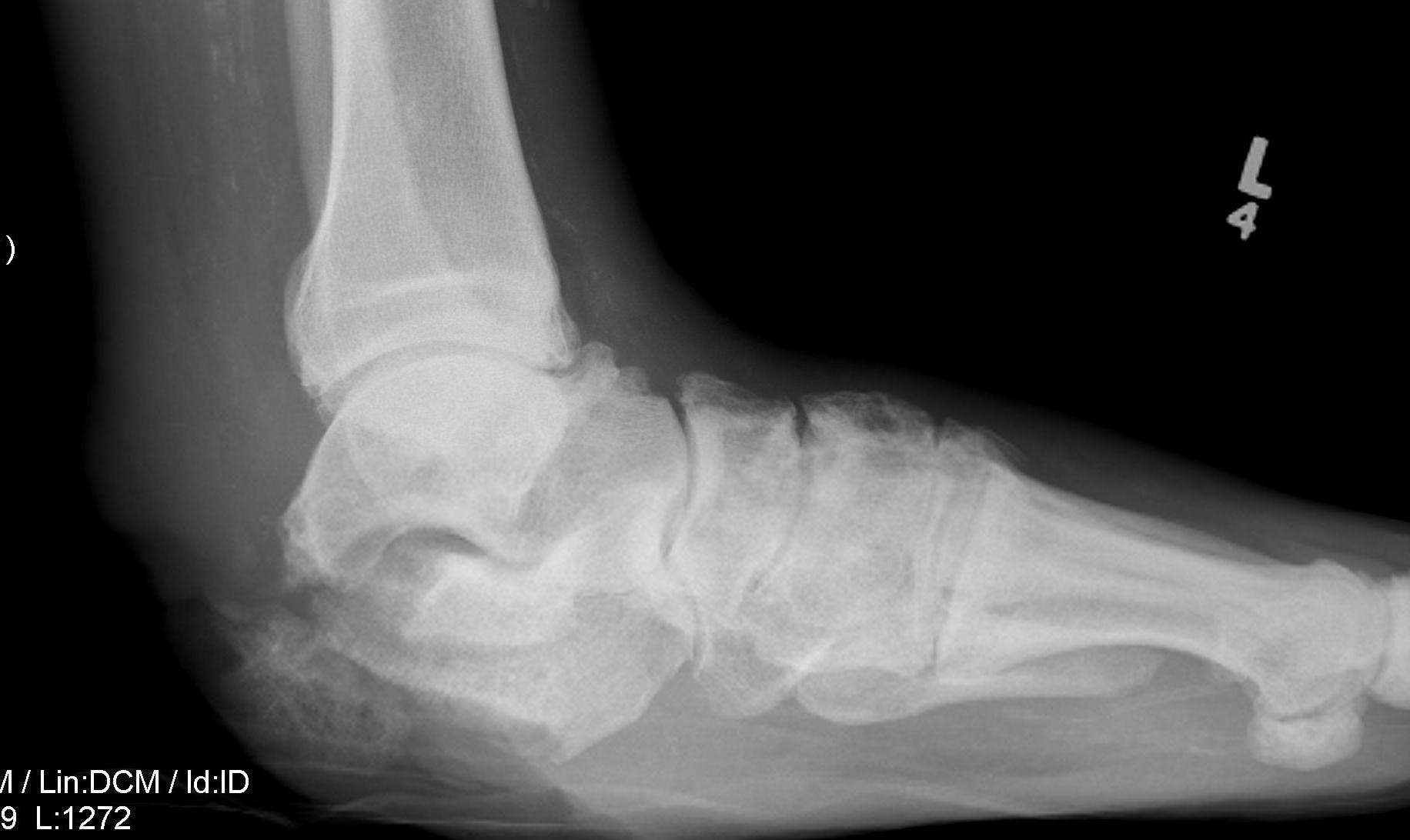
Calcaneal osteotomyelitis

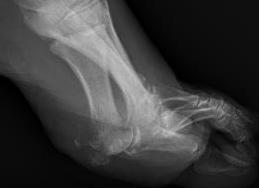
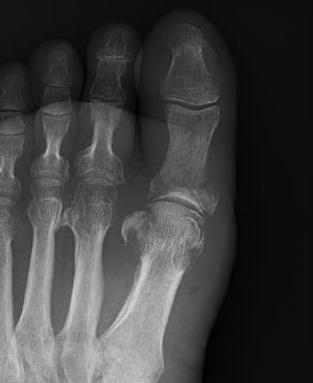
Diabetic foot ulcer with evidence of underlying osteomyelitis
Charcot arthropathy
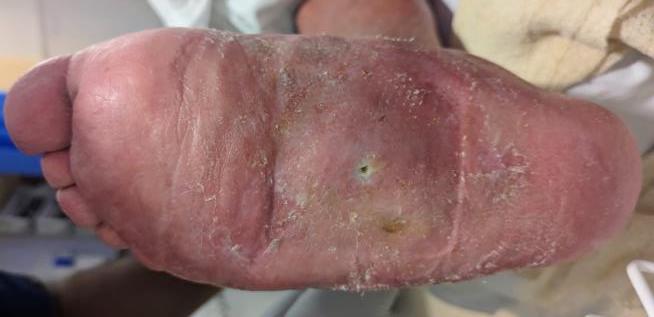
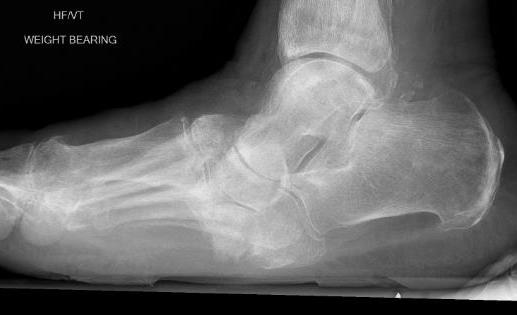
Midfoot ulcer with evidence of underlying Charcot arthropathy and midfoot collapse
www.boneschool.com/charcot-foot
Nonoperative management
Options
Treat infection
Wound dressing and ulcer debridement
Offload foot - orthotics / total contact casts / CROW walkers
Hyperbaric oxygen
Infection
| Microbiology | Antibiotics |
|---|---|
|
Acute mild infections - usually mono microbial - commonly S Aureus, Strep |
Combination oral antibiotics - Augmentin Duo Forte - Cephalexin plus Metronidazole - Ciprofloxacin plus Clindamycin (Penicillin Allergy) |
|
Chronic infections / ulcers - polymicrobial - gram positive cocci (Staph; Group B Strep) - gram negative (E Coli; Pseudomonas) - Anaerobes (ischaemic limbs, Bacteriodes fragilis) |
Severe infections - intravenous antibiotics - Timentin / Pip-Taz - Ciprofloxacin - Clindamycin |
Wound care and Ulcer debridement
Debridement
Wilcox et al JAMA Dermatol 2013
- 150,000 wound debridements
- increased healing with weekly (55%) versus less frequent debridement (28%)
Negative pressure therapy
Offload ulcers
Options
Total contact cast / Non removable walkers / removable walkers
- spread out force over a larger areag
- can reduce pressure by as much as 80 - 90%
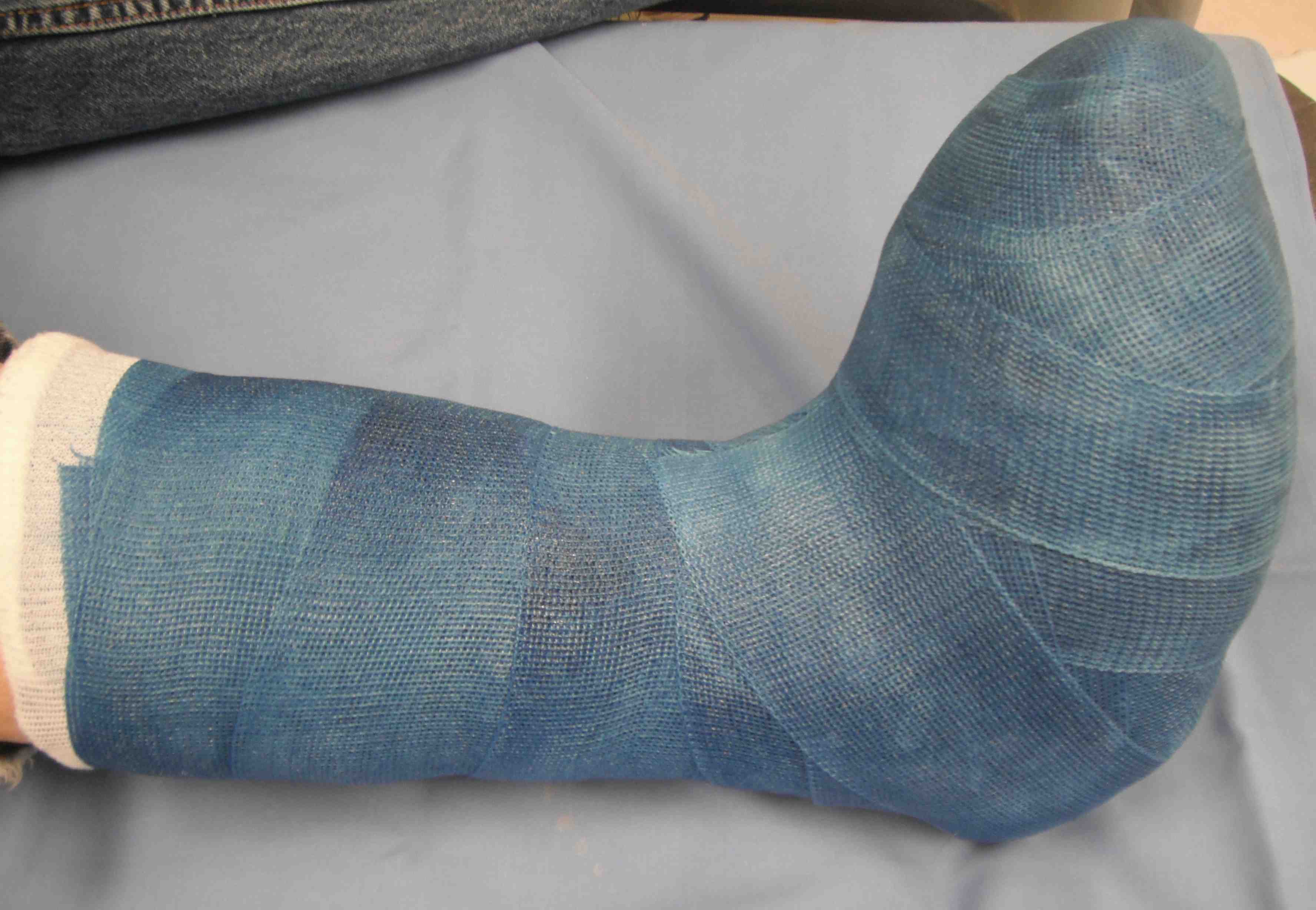

Results
Lazzarini et al Diabetes Metabol Res 2024
- systematic review of 194 studies
- increased wound healing with non removable devices (82 v 66%)
- likely due to compliance
Operative management
Options
Surgical debridement
Soft tissue releases - tendoachilles lengthening, toe flexor tenotomy
Bony realignment www.boneschool.com/charcot-foot
Amputations www.boneschool.com/diabetic-amputations
Fractures in Neuropathic / Diabetic feet
Principles
1. Augment ankle ORIF
2. Double time for sutures
3. Double immobilization period
4. Brace for 1 year after surgery
- to prevent late Charcot arthropathy
- assume Charcot joint will develop
